- support@locusassignments.com
Unit 3 Structure and Culture Organizations and Behavior Assignment
|
Program |
Diploma in Business |
|
Unit Number and Title |
Unit 3 Structure and Culture Organizations and Behavior |
|
QFC Level |
Level 4 |
Introduction
Organization consists of different people working in a group and collaboratively towards a common purpose or goals. In an organization, the behavior of the employees is important and thus organizational behavior deals with understanding of the behavior and working patterns of the employees in an organization. The structure and culture organizations and behavior study basically aims to discuss the structure of the organization and its relation to the culture of the organization in order to understand the impact on the performance. Leadership is basically involved in the organizational setting in order to influence the attitudes and behaviors of the people in the organization and get work done from them and thus contribute to the corporate objectives(Hayes, 2010). Also it discusses the various kinds of leadership that can be applied in the organization and their impact on the working and performance, motivation in an organization deals with driving the employees towards particular behaviors and goals. Thus the study aims to develop a complete understanding of the working relations in the groups and organization and use of modern technology in the organization, thus understanding the overall impacts on the performance.
Task 1
1.1different organizational structures and cultures
The structure in any organization basically denotes the way the various functions are arranged in an organization and the level of authority and relationships between them. Thus the structure of the organization can be based upon its size, nature of operations, geography of operations, products, complexity, etc and have been discussed as under following headings:
Divisional or heirarchial structure- this type of structure is relatively consisting of high line of commands between the top business management and the employees as employee are placed based on the need of organization as shown below.
Functional or flat structure- this type of organizational structure is relatively flat with grouping of people in functional departments with same nature of work like marketing, finance, etc and short line of commands and better communication between the staff and the top management.
Matrix structure: is a combined form of functional and divisional structures and people from different divisions and functional departments may be brought to work for specific task in organization (John, 2008). It is depicted by figure below.
Geographical structure: is the organization structure which is based on the geographical area of operations of the company and allow for better control and performance through regional structures (Hayes, 2010).
Product structure: is the organization structure based on the various products or lines of the company as shown below
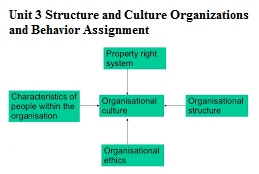
Culture: in any organization could be defined as values, norms, ideas, beliefs, etc that are transferred in the organization and had been initially established by the top management. This has an impact on how individuals interact with others and the key stakeholders in the inside and outside world.
Charles Handy in 1999 had given out mainly four types of cultures in an organizational setting as follows:
- Role culture: is where there is a narrow top management and number of roles in the organization which are played by the employees.
- Power culture: is like a spider web where the power is accumulated with the people at the centre of the organization and thus these organizations are capable to respond quickly to changes in the environment (Cunliffe et al, 2008).
- Task culture: is where the emphasis is on getting the tasks done and thus it is more or less oriented to the projects or tasks through effective team work.
- Person culture: is where the culture revolves around certain persons who act as focal points in the organization.
The organization structure and culture are interrelated and interdependent on each other as the structure decides the positions, role, responsibilities and attitudes in the organization employees which define its culture. A long hierarchy structure in the organization may be determinant of a power culture whereas wider organization structure believes in sharing of power and authority in culture more like work culture. Thus various kinds of structure and the culture are quite related to each other(Hayes, 2010).
In case of option, before Knud joined, the structure was a long hierarchy and there was high chain of command in the organization and functional structure in each department. The company was facing intense competition in the industry and culture was person and prestige oriented thus he turned the company from industrial to service based organization with a physical product, improved communication and use of technology and changed the structure to project structure with focus on customer orientation. This led to improvement in performance and productivity of the organization.
1.2 relationship between organizational structure and culture impact the performance
The structure and culture in an organization go hand in hand and if the organization has wide functional structure with division of authority and power to lower levels of management along with a culture towards open communications and performance then the organization performance will be impacted positively (Stewart, 2009).
Dependence of the employees on the organizational structure could be evident from the fact that for any business activity they have to go through level of commands and hierarchies. Thus the structure impacts all the aspects of functioning of the business. Workforce diversity is a common occurrence in the large organizations and thus adaptive culture helps in better performance of the employees from various countries. Acceptance to diversity as in most MNCs and changes in the culture helps in adapting to changes in the business environment thus impacting performance.
Empowerment to employees is a crucial factor in determining of the success and thus empowering of employees through open communication and low line of commands allow for better functioning and performance of organization. Thus if the structure is functional and culture allows authority to employees then employees will be performing better in such organization.
Customer services and satisfaction in any organization is dependent on its structure and open communication which is a part of culture and low level of hierarchies between the customer service staff and top managers allow for better services and satisfaction thus impacting performance of the organization (Kabelo, 2015). Strong culture allows for better services to the customers and better management of the competition thus allowing for better performance of the organization.
Efficiency of the performance in the organization is dependent on the behavioral patterns and policies prevalent in the culture including focus on promptness of services (Hayes, 2010).
As seen in case of Oticon, the company performance improve sufficiently on changes in structure from hierarchy to project orientation and culture from prestige and person oriented to power and task oriented on joining of Knud.
1.3 factors which impact individual behavior at work
The individual employee performance and behavior at the workplace can be based on various factors like
- Abilities: include the traits that any individual learns from his surroundings and may be by birth and includes physical and intellectual characteristics of an individual. Thus the behavior of an individual at workplace is impacted by their IQ level, physical attribute, etc.
- Perception: is a process where the individual converts the stimuli from the environment in to meaning. Thus individual may act differently to sounds, speech, taste, etc and this impacts their workplace behavior through impacting judgment.
- Attitude: is the overall outcome of the person cognitive process towards workplace aspects and thus impacts their behavior at workplace (Kabelo, 2015).
- Gender: impacts the workplace as the women are supposed to provide with essential holidays like maternity leave although men and women are equal in workplace.
- Race and culture: Race can be defined as some sort of common features in the people in a particular region or area like Indians, etc. Culture is consisting of all the beliefs, norms, traditions, etc and are learned and transferred from the family, teachers, parents and others in the society. As people from various cultures and race work together in the modern organizations thus the people must be open to accepting diversity.
Task 2
2.1 effectivenes of different leadership styles in different organizations
Leadership in the organizational context is use in driving the performance of the members of the team towards the organizational goals through having an influence on their behavior and attitudes to work.
Various leadership styles can be used based on the situation, as discussed below:
- Autocratic: is the leadership style where only one individual has all the powers of decision making in an organization and other employees have almost no power in decision making. This style can be applied in small organization but generally lacks in the creativity and commitments of the employees as seen in local grocery stores where owner commands over employees (Hayes, 2010).
- Democratic: style is where the employees have equal powers in the groups and the joint decision and consensus is used in the organization to improve performance.
- Paternalistic: is where the leader develops the position of the fatherly figure in the organization and leader provides care to their rights and interest.
- Laissez faire style: is where the leader is just an entity while all the responsibilities and powers vests in the hands of the employees to allow better accountability and performance.
- Transactional style: is where the relationship between the leader and the follower or the employees is seen as an exchange and employees work in exchange for monetary benefits (Fineman et al, 2010).
- Transformational style: is where the leader enacts by transforming the behavior and attitudes of the employees through his charisma and thus inspires and motivates them to perform better in the organization.
As seen in various leadership styles, the autocratic styles lack in creativity and commitments of the employees due to low participation and powers however the transactional style consider employees merely as a resource and do not focus on maintaining relationships with them. The transformational leadership style helps in bringing up the collaboration and participation of the employees through influencing their behaviors and attitudes (Hayes, 2010).
In case of Microsoft, the CEO Bill Gates uses democratic style of leadership and involves the employees in decision making while uses delegation in autocratic style to certain extent. This is the secret of the success of Microsoft as Gates is able to inspire the employees thus being good at delegation while involving them in decision making as well to improve commitment.
Fedex makes use of complex leadership involving affiliative style through development of trust, autocratic and democratic styles in its culture along with flat organization structure. The managers allow powers to the subordinates for delegating lower levels of employees. Both the fedex and Microsoft are good at managing the relationships with the employees but fedex is better in application of leadership style and thus generating of better working environment though both are profitable.
2.2 organizational theory underpins the pratice of management
Management is the art of getting the thing done in a desired manner and at correct time and place through use of various members in a team and thus it is the art of getting things done.
There can be various approaches to management in an organization based on various theories as:
- Administrative theory or approach: is where the organization consists of various functional divisions like marketing, Human resources, finance, etc in order to attain organizational objectives. This theory believes that administration is the most important in contributing to work or goal performance in the organization.
- Scientific approach: is based on Henri Fayol’s principles which include division of labor, delegation of authority, Espirit de corps, remuneration etc and the task is performed through performance of Planning, Organizing, Delegating, Controlling and Reviewing functions in order to allow for most effective utilization of the resources in the organization (Fineman et al, 2010).
- Human relations approach: of Elton Mayo is based upon maintenance of good relationships between the employees and the management in order to drive their performance and synergy towards the overall objectives lay down by the management.
In the case of Nice cars, the theory which was used involved Human Relations theory which focused on the development of good relations with the employees apart from providing for their training at company expenses and providing them job security along with other benefits like promotions and incentives for better performance whilst improving communications in the organization. This led to improvement in the performance and productivity of the organization (Hayes, 2010).
2.3 different approaches to management used by different organizations
Theory z/ japanese approach to management
This is based on certain assumptions like:
- Employee re interested in maintaining of cooperative relationship with the others in the organization
- They want job security apart from development and training needs
- They value social institutions like family and the personal life as well
- They have a good degree of self discipline, dedication and morale at work
- Allow collective decision making through joint mechanism (Stewart, 2009)
Western approach: With the rise of marketing globalization and the success of the foreign firms, people were getting keen to understand their approach to management of large organizations as compared to traditional Japanese management styles. While Japanese focus on joint consensus in decision making which is a time consuming process, the western style focuses on selling of decision or negotiation and thus time is used in acting on the decisions rather than reaching consensus. Thus western approach allows for effective decision making along with placing focus on the decisions impacting the policies and procedures in the organization. Also they provide for wider benefits of employees through income maintenance regimes. Thus the western approaches are quite impressive over the Japanese approaches which are time consuming and cumbersome.
In the case of Nice cars which was facing decline, the Japanese approach to management worked out through the provisions for training of the staff, providing them with job security, incentives and promotions for better performance and it helped in reduction of the error, reduction of investments in the inventory and improvement in the performance and attitudes of the workers and thus the whole organization. Thus the Japanese approach helped the organization in improving its performance in time of decline and recession.
Task 3
3.1mpact of different leadership styles on motivation in organization
According to studies, various leadership styles used in the organizations have different impacts on the level of motivation in the employees in the organization especially in the period of change.
- Employee oriented leadership: is focused on development of interpersonal relationships with the employees and taking care of their needs and interest in the organization in order to motivate them. Here the leader bears charisma and inspires others in the organization in order to perform better thus resulting in high performing employees which are concerned about their own growth while contributing to the productivity (Blanchard et al, 2009). In the periods of change such a leadership will help in accommodating the changes through inspiring employees to perform through charisma of the leader.
- Task oriented leadership: allows for ignorance of the needs and emotions of the employees and are more focusing on the targets to be done by them. Here the leader creates a powerful and autocratic position thus leading to fear and lack of motivations in the employees and thus they have low self esteem. In the period of change this autocratic leadership is less effective in managing the concerns of the employees and motivating them to accommodate with change. Thus employee oriented or democratic leadership is better in managing employee motivation in periods of change (Hayes, 2010).
3.2 different motivation theories at workplace
Motivation refers to the capability of the organization or leaders in eliciting favorable behaviors and performance towards the organizational goals and objectives. Various kinds of motivation theories at workplace are discussed as under:
Herzberg two factor theory: As per Fredrick Herzberg, the hygiene factors are those which when present produce a feeling of dissatisfaction amongst the employees but cannot yield complete satisfaction on not being present and includes salary, work conditions, etc (Rickards et al, 2009). The motivators are those factors which on being present can yield the feeling of satisfaction and willingness to perform the work in the organization and includes recognition for superior performance, growth at job, increased responsibilities, etc.
Theory x and y: According to theory X, the humans don’t like to work and thus they must be forced and directed to work thus this can be done through a controlled or authoritative type of work culture as in case of Toyota. According to theory Y, the employee performance should come out naturally and punishment or threat is not the appropriate method of eliciting work performance from employees. However the rewards make them more committed to the organization. Thus the organization must focus on personal needs of the employees in order to drive their performance (Blanchard et al, 2009).
In the case of the benefits Agency, the approach to motivating the staff was the theory X and Y and thus the management allowed for creativity and authority of the employees and paying for the right person at the right time and position in the organization. As previously the organization had controlled work environment with authoritative type of work culture and following of rules and regulations was strict which led to low motivation levels in employees at Benefits Agency.
As per Herzberg two factor theory both these factors affect employee motivation and performance through creating a feeling of happiness and satisfaction and limiting the elements bearing negative impact on performance. Thus in this theory the focus is on minimization of elements causing dissatisfaction in the employees to motivate them. While in theory X and Y, the motivation comes out from needs of the employees as managed through rewards and punishments. The theory Y entails generation of employee performance through rewarding as per their needs (Hayes, 2010).
3.3 usefulness of motivation theory for managers
By having an understanding of the motivation theories, the managers can understand the factors that motivate or de-motivates the employees. Motivation begins with a need or want and through understanding of needs, managers can improve the productivity through drives that help in eliciting desired behaviors from employees in organization. This helps in developing manager understanding psychological factors that impact the employee performance and behaviors as work as involving desire for
- Money or compensation
- Success
- Recognition
- Job satisfaction
- Development needs (Steward, 2009)
Thus the managers can elicit better productivity by making use of motivation theories at workplace. By understanding various psychological needs of motivating employees, desired behaviors can be elicited by stimulating the employees in correct manner. The needs and wants of employees can be tackled through designing of good incentive plan.
The managers can aim for high performing teams in the organization through developing motivation and providing for the needs of employees in order to improve the productivity in the organization. As per the theory of Taylor, the money is an important motivation factor in the employees working in the organization however as per the Herzberg theory the employees can be motivated by reducing the dissatisfaction base on Hygiene factors and motivation depends on the other factors (Ryan, 2014).
In case of Benefits Agency, the managers were able to motivate the employees through providing them right remunerations for the right job and at the right time and allowing for creativity and innovation in the job as previously the employees were supposed to stick to rules and regulations and were lacking due motivation. However, two factor theory of Herzberg is better in motivating employees at Benefits agency by reducing dissatisfaction causing factors like strict regulations and lack of authority and participation (Hayes, 2010).
Task 4
4.1 nature of groups and group behavior within organization
In an organization, groups are referred to as a collection of people who come together to attain common purpose or functions and work together with other members in the group to attain those objectives. This helps in better functioning of the tasks as individual alone cannot do all the things and synergy is affected through sharing of knowledge, skills and information between the members of the groups through team working.
- According to Tuckman’s Model of group model, the following stages are important in formation and performance of a group (Tuckman, 2000):
- Forming is where the accepted behaviors are identified by the members of the group and try to behave accordingly in the group.
- Storming is where the leadership and the roles of the various members in the groups are clearly defined and disagreements are worked out.
- Norming is the stage where there is development of close relationships amongst the group members.
- Performing is the stage where the members perform in the group in order to attain the goals and targets.
- Adjourning is the last stage and the group members may or may not be satisfied with others and group performance. After this stage the group will cease to exist through interpersonal relations may remain for future (Hayes, 2010).
Various kinds of groups exist in any organization but mainly they can be divided as formal and informal groups:
Formal groups: are created by the management of the organization and they are assigned with certain goals and objectives to be achieved. Here the role and responsibility of each member in the group is assigned by the top managers and they are supposed to work accordingly. It can further be of following types:
- Command groups: are formed and designated in the organization structure and they are permanent in an organization like Customer Services Handling employees in group.
- Task groups: have been formed in the organization for performance of a limited time or limited to a task or project. They are temporary in nature and have huge impact on performance of the organization (Hayes, 2010).
Informal groups: are not appoint or allocated by the organization but are formed by the interactions of the people in the organization.
- Friendship groups: consist of friends who may have something in common like age, religion, attitude, etc.
- Interest groups:
Teams and groups: A team is a group of people coming together for common objectives and joint for collective attainment of the common goals and targets however every group is not a team but every team is definitely a group and thus the effective teams are characterized by (Stewart et al, 2009)
- High level of performance
- Sharing of knowledge and skills
- Collective attainment
- Member satisfaction
- Synergy in performance
4.2 factors that promote or inhibit development of effective teamwork in organization
In case of large organizations, the managers get the tasks accomplished through the help of the various employees n the teams and thus they must focus on developing of effective team working in the team and minimizing of the friction between them. Thus the major factors that have a bearing on the working of the teams can be understood through team effectiveness model.
In the case of ZICO computers, development of software named Element Management Framework (EMF) consisted of a virtual team of eight people located at four different location and they never met. Though each and every member were well trained and experienced in their own functions but their ideas may compete specially in the storming stage and thus conflicts may arise in the effective working of the team in a virtual environment (Fineman et al, 2010).
The main factors that can promote or inhibit the performance of the team as in case of Zico Computers can be discussed as below:
- Workforce diverity: the people in the team may be of different age, gender, religion, culture, nationality, etc and thus the diversity contributes to the creativity and fresh ideas in the team work while the conflicts may bear a negative impact on its own functioning.
- Communication: it is important that the group members must be openly communicating and asking for information or even sharing skills, ideas, etc in order to allow better function of the team thus communication is an important consideration (Hayes, 2010).
- Trust: it is important that all the members of the team trust each other and provide for sharing of information and skills amongst themselves to allow synergy and collaborative commitment towards common goals.
- Attitude: the positive attitudes of the team members towards the joint performance of the task functions help in better and timely completion of goals and vice versa.
- Leadership: In order to collaborates the team work, a good leader must be capable of
- Handling conflict between team members
- Transforming their behaviors and attitudes
- Drive collective efforts and synergy in team performance
- Allow democracy in decision making
- Allow for training and motivation of team members (Hayes, 2010)
4.3 impact of technology on team functioning
The advent of modern technology has turned the world in a global village and communications and exchanges can take place from and to any part of the world almost instantly. As the modern organizations are dispersed in to various geographical areas thus the use of technology through the mobile communication, e-mails, chats, etc has become increasingly important as seen in case of virtual team at Zico computers which consisted of members from four different locations.
- Messaging: is very important aspect of business functioning in the modern world and this allows the managers to assign tasks, get information on progress, whereabouts, status of work, etc at just clicks on devices thus allowing for better functioning of the organization functions.
- Emails and mobile communications: help in better coordination between the team members in the organization through being in contact through mails and calls and allows for remote location operations of the employees.
- Sharing files on internet and intranet: has become a revolution and thus the information based files can reach in seconds to various people in the organization located in far off places (John, 2008).
This has led to formation of Virtual teams as in Zico computers which allows people dispersed in different locations worldwide to perform together for project functions in an organization. Thus the use of the modern technology has led to close cooperation and team working possible in the members of the virtual teams however the nature of work, nature of team members effect the performance of the virtual teams and their collaboration. Thus this kind of systems brings in positive contribution to the organizational performance somehow.
However it had been observed that the working in virtual teams is slow and time taking due to differences in demographic and other factors of the team members and lack of physical contact
Conclusion
The study basically discussed the various types of cultures and structures and their impact on the overall performance of the organization. The flat organizational structure allow for better creativity, communication through reduction of the line of commands and thus allows for better functioning and control in the organization. The culture of the organization must thus promote open communication, creativity and high focus on the performance and productivity through best utilization of the resources. The leadership styles are important in influencing the behaviors and attitudes of the employees or team members in an organization. Motivation is the understanding of the needs of the employees and thus allowing for better performance through provision for their needs like salary, rewards. Incentives, recognition, promotions, etc and the managers must be well at making use of the motivation theories in improving the team performance. The group of people in organization form effective team based on synergy, collaboration and thus collective efforts through sharing of information and knowledge and skills amongst themselves.
References
Cunliffe, A.L. (2008). Organization Theory, London: Sage Publications Ltd. Pp 57-94
Fineman, S., Gabriel, Y., Sims, D. (2010). Organizing & Organizations, 4th Edition, London: Sage Publications Ltd. Pp 111-27
Compare And Contrast Different Organizational Structure & Culture(online) available at http://www.lawteacher.net/free-law-essays/international-law/compare-and-contrast-different-organizational-structure-and-culture-law-essay.php last accessed on 30 July, 2016
Stewart, G.L., Manz, C.C., Sims, H.P. (2009). Team Work and Group Dynamics, New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc. pp 310-27
Hayes, J. (2010). The Theory and Practice of Change Management, 3rd Edition, Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan Ltd. Pp 302-319
BPP Learning Media Ltd. (2010). Organisational Culture. Business Essentials, Organisations abd Behaviour (p.104). London.
Ryan, C. (2014) (online) available at .http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Treehouse_(company)#Culture. last accessed on 30 July, 2016
Theory Z (2016) (online) available at http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/theory-Z.html last accessed on 30 July, 2016
Blanchard, K. and Parisi-Carew, E. (2009) The One Minute Manager Builds High Performing Teams, William Morrow, pp 282-99
Rickards, T., & Moger, S., (2000) ‘Creative leadership processes in project team development: An alternative to Tuckman’s stage model’, British Journal of Management, Part 4, pp273-283
Need Help with Your Assignment?
Get expert guidance from top professionals & submit your work with confidence.
Fast • Reliable • Expert Support
Upload NowDetails
Other Assignments
Related Solution
Other Solution











